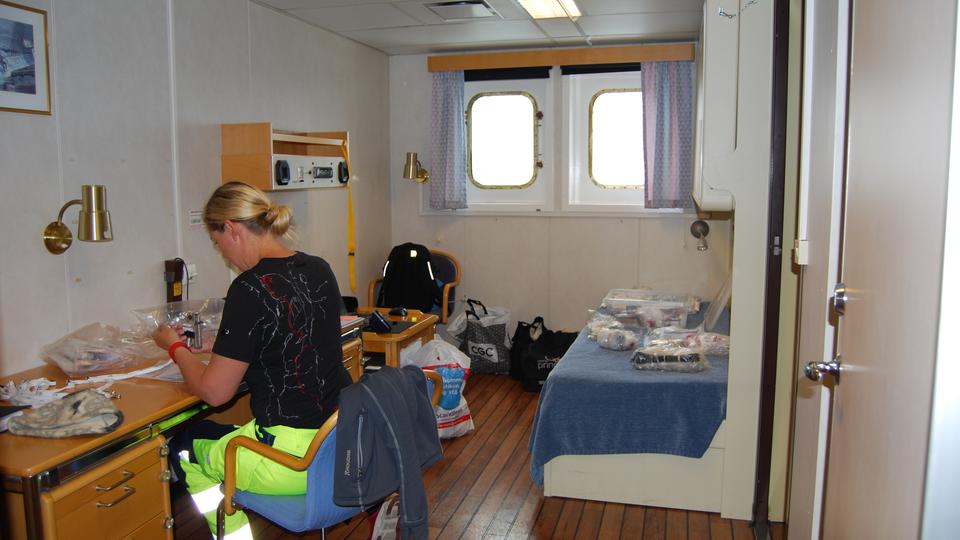
Researcher Cecilia Österman collects analysis test tubes that measure air pollution in the cabin
Measurement and analyses of air quality parameters
Det finns olika sätt att undersöka vilka luftföroreningar som förekommer i innemiljön. I det här avsnittet ges exempel på hur mätningar går till, vilka laboratorier som kan hjälpa till med mätning och analys av olika ämnen, samt information om vad som ska ingå i en mätrapport.
Planning the measurements
There are several ways to investigate air pollutants in the indoor environment. The Swedish Work Environment Authority's regulations on limit values for respiratory exposure in the work environment contain rules on which substances may need to be measured depending on the type of air pollutant, how the measurement should be planned and how it should be carried out.
If the aim of the investigation is to assess the relationship between the concentration and the limit values, the measurements must be carried out using personal samplers placed in the breathing zone. The measurements should be planned together with the workers concerned.
Contents of the measurement report
In order for the exposure measurement to be used for an overall assessment of the chemical risks of the work environment, the results of the measurements must be documented in a measurement report, which must contain at least the following information:
- Where the measurements were carried out in relation to where the workers normally spend their time.
- The conditions at the workplace during the sampling, such as which engines were running at what times and the functioning of the ventilation system.
- How the staff were working in the room, an assessment of the staff's physical workload, which can affect the uptake of hazardous substances, and whether they were wearing personal protective equipment.
- What other exposures occur simultaneously and have a synergistic hygienic effect.
- A comparison with previous surveys or other investigations to put the results into perspective.
- What action is recommended in response to the results of the measurements.
Methods for measuring air pollutants in general indoor environments can also be applied to air quality studies on ships. Measured concentrations can be compared with occupational health and safety limits in work areas or recommended guidelines in living areas.
How to make measurements
Some on-board measurements of air pollutants and indoor climate parameters can easily be carried out using passive samplers or simple sensors. The advantage of passive samplers is that they require no power and are small and quiet. Some other measurements, such as particulate matter, require more sophisticated instruments operated by experienced personnel. Instructions for measuring gaseous and particulate air pollutants commonly found on ships are described in the following sections. The information is categorised according to the type of sampler, sensor or instrument required for the different measurements.
Results for airborne pollutants are given as concentrations in µg/m3 (micrograms per cubic metre). The concentration is an average over the sampling period.
Laboratories
Laboratories that can carry out measurements and analyzes of air pollution:
- Arbets- och miljömedicin Göteborg: formaldehyde, elemental carbon, inhalable dust, respirable dust and total dust.
- Arbets- och miljömedicin Syd: inhalable dust, respirable dust, total dust, naphthalene and benzo(a)pyrene.
- IVL Swedish Environmental Research Institute: nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide, carbon monoxide, volatile organic compounds (VOC), particles, formaldehyde, carbon dioxide, temperature and relative humidity.