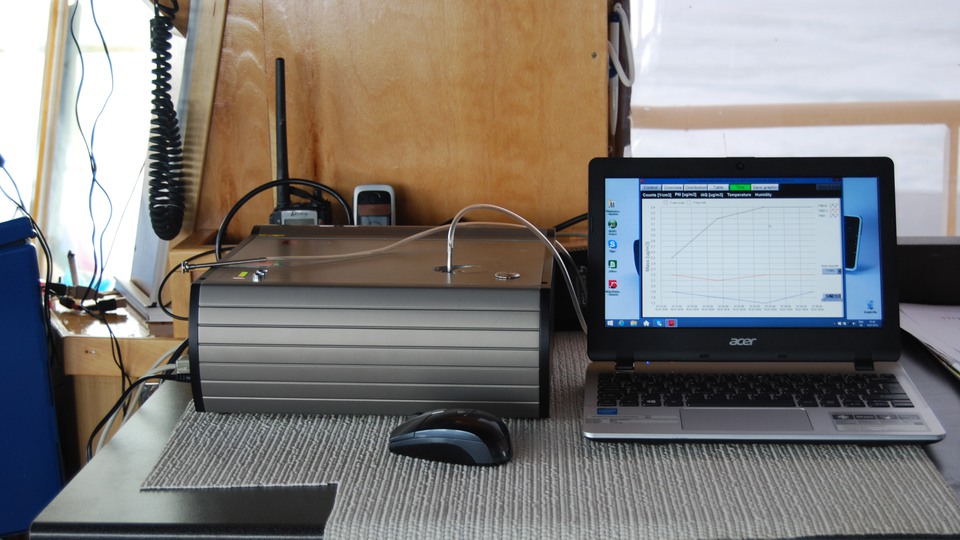
Seafarers' guide database
The database compiles measurement results from air pollution surveys on board about twenty ships. Measurements were carried out with stationary samplers in various locations on board and with personal samplers to investigate the exposure of seafarers.
For comparison, the database also contains data on the levels of these air pollutants measured in homes and offices, as well as for some other types of occupations. There is also a simple tool to calculate the risk posed by the levels of different chemicals.
The database has four parts:
- Site measurements on-board: contains information on ship type, fuel type, location of on-board measurements, temperature, relative humidity and levels of air pollutants and particles.
- Exposure in other occupations: contains data on measured levels of personal exposure to the selected air pollutants in the following occupations: cooks, police officers, firefighters and workers who are exposed to diesel exhaust during their work. The data have been collected from the scientific literature.
- Seafarers’ personal exposure: includes data on ship type, fuel type, ship function and levels of selected air pollutants.
- General indoor environments: includes data on temperature, relative humidity and concentrations of air pollutants and particles in homes and offices. The data have been collected from the scientific literature.
Graphical presentation of all measured data
The Seafarers' Guide database is presented graphically
 External link, opens in new window. n the form of box plots describing the distribution of the measured values. Stationary measurement graphs show data from all stationary on-board measurements on all ships, together with data for general indoor environments in homes and offices. Personal exposure plots show data from exposure measurements on seafarers, regardless of their function, on all ships, together with exposure data from other occupations that may be affected by exposure to the substances included in our study. These workers are cooks, police officers, firefighters, industrial workers and transport workers. The measured parameters included in the stationary measurements and personal exposures are shown in the table below.
External link, opens in new window. n the form of box plots describing the distribution of the measured values. Stationary measurement graphs show data from all stationary on-board measurements on all ships, together with data for general indoor environments in homes and offices. Personal exposure plots show data from exposure measurements on seafarers, regardless of their function, on all ships, together with exposure data from other occupations that may be affected by exposure to the substances included in our study. These workers are cooks, police officers, firefighters, industrial workers and transport workers. The measured parameters included in the stationary measurements and personal exposures are shown in the table below.
The measured concentrations are presented in one or two box plots per measured parameter, which can be selected from a drop-down menu. The box plots show how some selected percentiles relate to each other. The centre line of the 'box' shows the median value of the measurement, the top and bottom of the box correspond to the 75th and 25th percentiles and the 'whiskers' show the 90th and 10th percentiles. The points outside the lines represent extreme values. For comparison, the recommended guideline values for indoor air are shown as red dashed lines. The number next to the line indicates the guideline value. Comparisons with Occupational Exposure Level (OEL) values are not included in the diagram, as all results are well below the limit values. You can watch an instructional video on using the database visualization tool.
If you are interested in a more detailed analysis of data such as nitrogen dioxide levels in engine rooms of heavy fuel oil ships, you can use the filter function in Excel to select only the part of the database you are interested in.
How does Seafarers' guide database work? Watch the video below.
Cumulative risk index
Exposure to air pollution on ships involves simultaneous exposure to several different substances that may have similar effects, a so-called additive health effect.
A model known as the cumulative risk index (CRI) is used to assist in the assessment and evaluation of the health risk posed by combined exposure to several chemical substances. The risk index is a weighted sum of the concentrations of the individual substances or constituents included in the exposure. The CRI is calculated as the sum of ratios between measured levels and their respective recommended health-based guideline levels.
Details of how the cumulative risk index is calculated based on measured levels of nitrogen dioxide (NO2), benzene, benzo(a)pyrene and naphthalene, and how it varies between different ships, positions (officers, crew) and departments (deck, engine, quartermaster) can be found in the report Riskbedömning av svenska sjömäns yrkesmässiga exponering för toxiska luftföroreningar (In Swedish)
 Pdf, 2 MB..
Pdf, 2 MB..
Risk Index – a tool for calculating and assessing air pollution risks
We have developed a tool called Risk Index External link, opens in new window. that facilitates the calculation and assessment of the risks that concentrations of different air pollutants can cause. The tool is based on the Cumulative Risk Index and allows you to select reference values for the general indoor or work environment, type of air pollutant and then enter your own measured values. Pay attention to the units for concentrations, which should be µg/m3 (micrograms per cubic metre). A risk ratio is then calculated for each air pollutant using the relevant guideline values for the indoor environment or OELs for the work environment. The risk ratios are combined into a cumulative risk index, either for the indoor environment or for the working environment. If the risk index is greater than 1, the exposure needs to be further investigated and measures to reduce exposure planned and implemented. A risk index below 1 means that exposure is so low that it is currently considered acceptable by society. You can watch an instructional video on using the tool for risk assessment of the levels of the air pollutants.
External link, opens in new window. that facilitates the calculation and assessment of the risks that concentrations of different air pollutants can cause. The tool is based on the Cumulative Risk Index and allows you to select reference values for the general indoor or work environment, type of air pollutant and then enter your own measured values. Pay attention to the units for concentrations, which should be µg/m3 (micrograms per cubic metre). A risk ratio is then calculated for each air pollutant using the relevant guideline values for the indoor environment or OELs for the work environment. The risk ratios are combined into a cumulative risk index, either for the indoor environment or for the working environment. If the risk index is greater than 1, the exposure needs to be further investigated and measures to reduce exposure planned and implemented. A risk index below 1 means that exposure is so low that it is currently considered acceptable by society. You can watch an instructional video on using the tool for risk assessment of the levels of the air pollutants.